Facebook ditches Bing, 800M users now see its own AI text translations

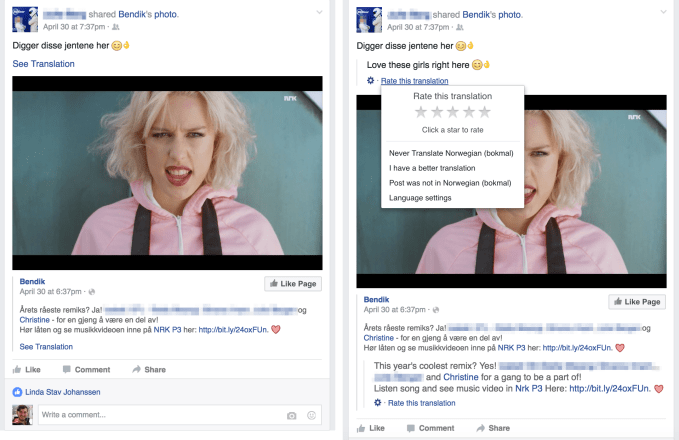
Machine learning is accomplishing Facebook’s mission of connecting the world across language barriers. Facebook is now serving 2 billion text translations per day. Facebook can translate across 40 languages in 1,800 directions, like French to English. And 800 million users, almost half of all Facebook users, see translations each month.
That’s all based on Facebook’s own machine learning translation system. In 2011 it started working with Microsoft Bing to power translations, but has since bene working to transition to its own system. In December 2015, Facebook finally completed the shift, and now exclusively uses its own translation tech.
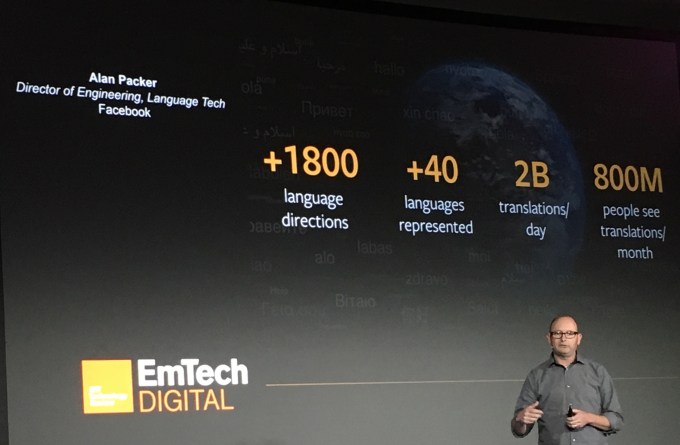
Alan Packer, Facebook’s director of engineering for language technology, revealed this progress today at MIT’s Technology Review’s EmTech Digital conference in San Francisco. The conference has a big focus on artificial intelligence, machine learning and other cutting-edge ways to parse data.
[Update: After his talk, I sat down with Packer, who told me about Facebook ditching Bing-powered translation. This article has been updated to add info from him.]
Earlier, Pinterest’s head of product Jack Chou revealed that just six months after launching its visual search feature, Pinterest sees 130 million visual searches every month. The product was built by a small team of four, and allows people to search using a source image instead of just text. Pinterest also now has 50 million buyable pins from 20 million merchants.
Facebook’s ability to not only translate but understand the content of text and images could lead to big advances in the relevancy of the News Feed. Packer explained that if Facebook can understand a post is asking for recommendations of hotels in Paris, it could surface that to friends it knows recently visited Paris, suggest a particular friend to ask or recommend making a related search for public posts of recommendations.
Facebook was an early pioneer of online translation, building a crowdsourcing tool to get users around the world to translate its interface’s text into their local tongues. In 2011, Facebook began using automated systems to translate users’ posts and comments in the News Feed.
Last year, Facebook acquired Wit.ai, a startup using understanding of natural language in text and voice to power new user interfaces. Google and Microsoft/Skype have also been aggressively pursuing translation tools to unite the world across borders.

Facebook initially turned to Bing because “we didn’t have our own technology but saw that there was value in it. We did a deal, turned it on, and got a lot of usage” Packer tells me. The problem was that Bing was built to translate more properly written website text, not the way humans talk to each other. Packer says Bing “didn’t do well on slang, idioms, and metaphors. We really needed to train on our own data.”
So Facebook looked at the languages most in need of translation, and got cranking on building a version of the tech that did better than Microsoft. “We did our own internal bake-off. When we could show it was better than Bing [for a specific language to language translation], we would turn Bing off and replace it with our own service.
Now, the translation is fully rolled out for 1800 different translation permutations. When Facebook is confident its translation is perfect, it will automatically show the translation by default with an option to “See Original”, and only shows the opt-in “See Translation” button when it thinks it might have errors.
Packer tells me other Facebook teams from anti-spam and policy enforcement to acquisitions like Instagram are now considering how they could integrate translation.
The motive is obvious, socially conscious and lucrative. Facebook’s mission is to make the world more open and connected. I asked Packer how translation plays into that, and he said, “The mission of the translation team is removing language as a barrier to making the world more open and connected.”
While he didn’t have concrete numbers, Packer says that access to the translation product leads users to “have more friends, more friends of friends, and get exposed to more concepts and cultures.” And the company knows it’s grown important to users, because “when we turned it off for some people, they went nuts!” The more people across the world that Facebook users can connect with, the longer they’ll spend on the social network, and the more revenue-earning ads they’ll see.
We’re rapidly approaching an era of the AI haves and have-nots. Tech giants who don’t have the engineering prowess to parse the meaning of their content or information won’t be able to deliver it to users as effectively. Companies like Google, Facebook and Microsoft could flourish while others more strapped for cash and resources to invest in research stumble.









